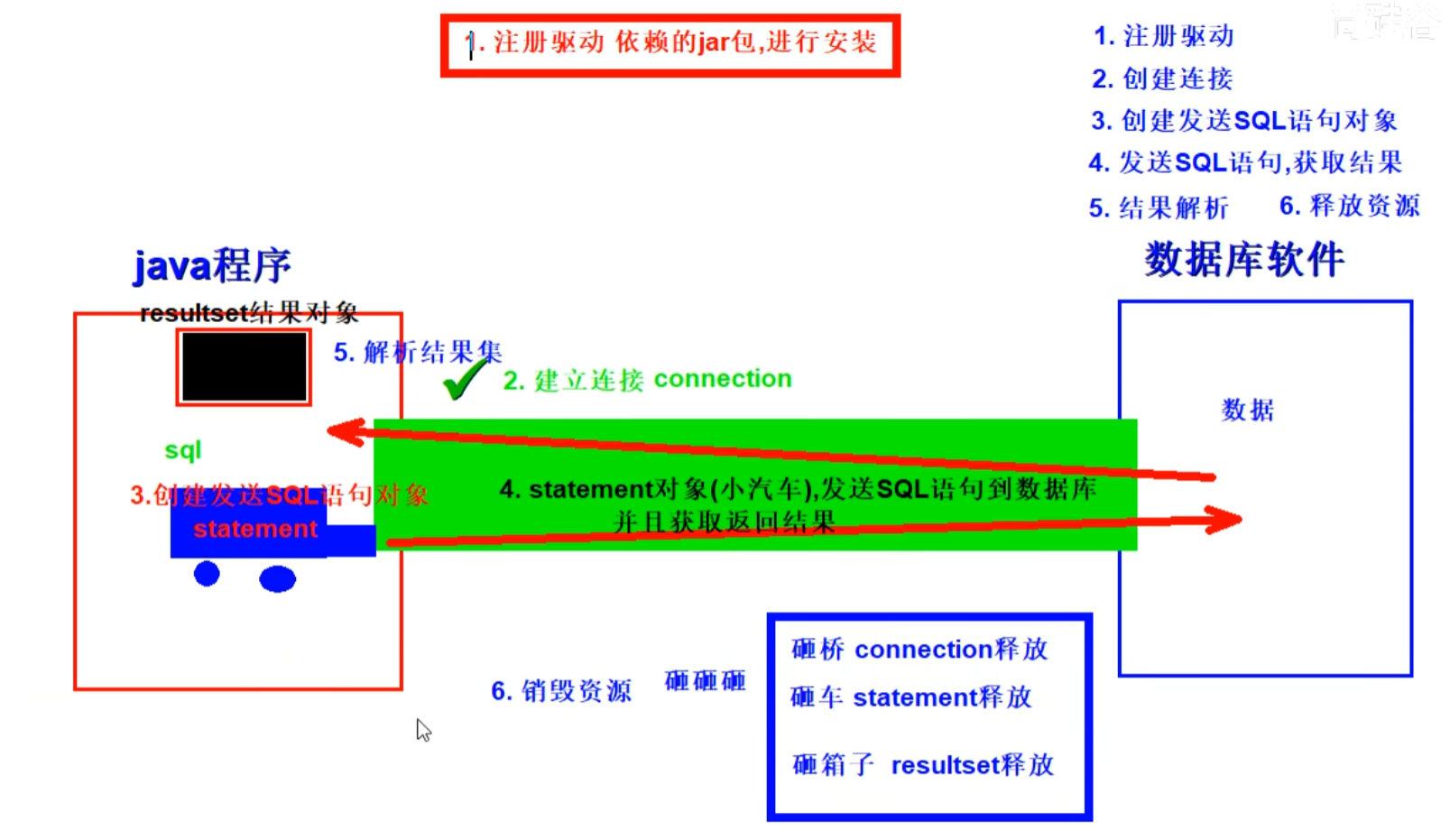
基本步骤
1.注册驱动
准备数据库的建表语句
1 2 3 4 5 CREATE TABLE user ( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR (100 ), PRIMARY KEY (id) );
通过反射机制+静态代码块初始化数据库驱动。
通过反射的方式读取文件中的数据库驱动类路径,,方便外部化配置
使用静态代码块,在类加载的时候数据库初始化驱动只需要初始化一次,实现数据库驱动的初始化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java .sql.Driver { public Driver () throws SQLException { } static { try { DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver ()); } catch (SQLException var1) { throw new RuntimeException ("Can't register driver!" ); } } }
2.获取连接 Connection是与特定数据库连接回话的接口,使用的时候需要导包,而且必须在程序结束的时候将其关闭。getConnection方法也需要捕获SQLException异常。
1 Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/exam?characterEncoding=UTF-8" , "root" , "admin" );
通过加载外部配置建立数据库连接的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Test public void testConnection5 () throws Exception { InputStream is = ConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties" ); Properties pros = new Properties (); pros.load(is); String user = pros.getProperty("user" ); String password = pros.getProperty("password" ); String url = pros.getProperty("url" ); String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass" ); Class.forName(driverClass); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); System.out.println(conn); }
其中配置文件如下
1 2 3 4 user=root password=abc123 url=jdbc:mysql: driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
3.创建发送sql语句对象 创建Statement或者PreparedStatement接口,执行SQL语句
使用Statement接口 Statement接口创建之后,可以执行SQL语句,完成对数据库的增删改查。其中 ,增删改只需要改变SQL语句的内容就能完成,然而查询略显复杂。在Statement中使用字符串拼接的方式,该方式存在句法复杂,容易犯错等缺点,具体在下文中的对比中介绍。所以Statement在实际过程中使用的非常的少,所以具体的放到PreparedStatement那里给出详细代码。
字符串拼接方式的SQL语句是非常繁琐的,中间有很多的单引号和双引号的混用,极易出错。
使用statement直接拼装出最终的sql查询语句容易产生sql注入。以下是sql注入的一个典型例子.SQL 注入 是利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查,而在用户输入数据中注入非法的 SQL 语句段或命令(如:SELECT user, password FROM user_table WHERE user=’a’ OR 1 = ‘ AND password = ‘ OR ‘1’ = ‘1’ ) ,从而利用系统的 SQL 引擎完成恶意行为的做法
Statement 实现批量插入时,效率较低
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 public class StatementTest { @Test public void testLogin () { Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print("用户名:" ); String userName = scan.nextLine(); System.out.print("密 码:" ); String password = scan.nextLine(); String sql = "SELECT user,password FROM user_table WHERE USER = '" + userName + "' AND PASSWORD = '" + password + "'" ; User user = get(sql, User.class); if (user != null ) { System.out.println("登陆成功!" ); } else { System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!" ); } } public <T> T get (String sql, Class<T> clazz) { T t = null ; Connection conn = null ; Statement st = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { InputStream is = StatementTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties" ); Properties pros = new Properties (); pros.load(is); String user = pros.getProperty("user" ); String password = pros.getProperty("password" ); String url = pros.getProperty("url" ); String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass" ); Class.forName(driverClass); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); st = conn.createStatement(); rs = st.executeQuery(sql); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if (rs.next()) { t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i++) { String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(t, columnVal); } return t; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null ) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (st != null ) { try { st.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null ) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return null ; } }
使用PreparedStatement接口(常用) 与 Statement一样,PreparedStatement也是用来执行sql语句的与创建Statement不同的是,需要根据sql语句创建PreparedStatement。除此之外,还能够通过设置参数,指定相应的值,而不是Statement那样使用字符串拼接。
可以通过调用 Connection 对象的 preparedStatement(String sql) 方法获取 PreparedStatement 对象
PreparedStatement 接口是 Statement 的子接口,它表示一条预编译过的 SQL 语句
PreparedStatement 对象所代表的 SQL 语句中的参数用问号( ? )来表示,调用 PreparedStatement 对象的 setXxx() 方法来设置这些参数
setXxx() 方法有两个参数,第一个参数是要设置的 SQL 语句中的参数的索引(从 1 开始),第二个是设置的 SQL 语句中的参数的值
优势:
能够通过检验条件数量防止sql注入。PreparedStatement 可以防止 SQL 注入,解决拼串问题
避免了直接拼装字符串的繁琐。代码的可读性和可维护性。
PreparedStatement 能最大可能提高性能:
DBServer 会对预编译语句提供性能优化。因为预编译语句有可能被重复调用,所以 语句在被DBServer的编译器编译后的执行代码被缓存下来,那么下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句就不需要编译,只要将参数直接传入编译过的语句执行代码中就会得到执行
在 Statement 语句中,即使是相同操作但因为数据内容不一样,所以整个语句本身不能匹配,没有缓存语句的意义.事实是没有数据库会对普通语句编译后的执行代码缓存。这样 每执行一次都要对传入的语句编译一次(语法检查,语义检查,翻译成二进制命令,缓存)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 增删改操作DML public void update (String sql,Object ... args) { Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement ps = null ; try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ;i < args.length;i++){ ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps); } } 查询操作DQL public <T> T getInstance (Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) { Connection conn = null ; PreparedStatement ps = null ; ResultSet rs = null ; try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i + 1 , args[i]); } rs = ps.executeQuery(); ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if (rs.next()) { T t = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0 ; i < columnCount; i++) { Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1 ); String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1 ); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(t, columnVal); } return t; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } return null ; }
4.发送sql语句并获取返回结果 ResultSet
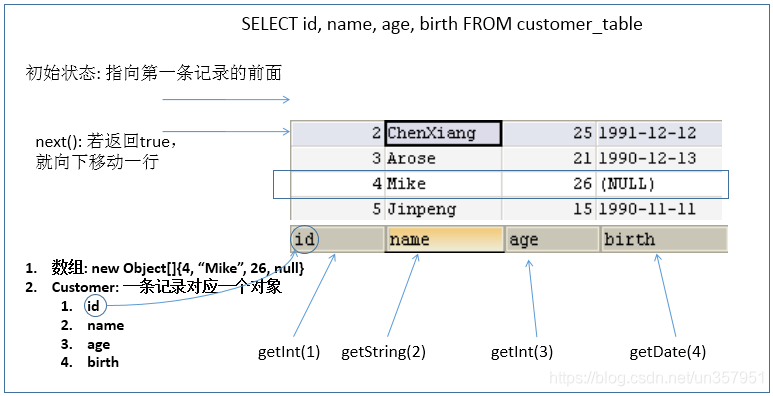
查询需要调用 PreparedStatement 的 executeQuery() 方法,查询结果是一个ResultSet 对象
ResultSet 对象以 逻辑表格的形式 封装了执行数据库操作的结果集,ResultSet 接口由数据库厂商提供实现
ResultSet 返回的实际上就是一张数据表。有一个指针指向数据表的第一条记录的前面
ResultSet 对象维护了一个指向当前数据行的 游标,初始的时候,游标在第一行之前,可以通过 ResultSet 对象的 next() 方法移动到下一行。调用 next() 方法检测下一行是否有效。
若有效,该方法返回 true,且指针下移。相当于 Iterator 对象的 hasNext() 和 next() 方法的结合体
当指针指向一行时, 可以通过调用 getXxx(int index) 或 getXxx(int columnName) 获取每一列的值。例如: getInt(1) , getString(“name”)
1 stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
可用于获取关于 ResultSet 对象中列的类型和属性信息的对象 ( 结果集数据的元数据 )
ResultSetMetaData meta = rs.getMetaData();
getColumnName(int column):获取指定列的 名称
getColumnLabel(int column):获取指定列的 别名
getColumnCount():返回当前 ResultSet 对象中的列数
getColumnTypeName(int column):检索指定列的数据库特定的类型名称
getColumnDisplaySize(int column):指示指定列的最大标准宽度,以字符为单位
isNullable(int column):指示指定列中的值是否可以为 null
isAutoIncrement(int column):指示是否自动为指定列进行编号,这样这些列仍然是只读的
针对于 表的字段名与类的属性名不相同 的情况:
必须在声明 sql 时,使用类的属性名来命名字段的别名
使用 ResultSetMetaData 时,需要使用 getColumnLabel() 来替换getColumnName(), 获取列的别名。如果 sql 中没有给字段其别名,getColumnLabel() 获取的就是列名
5.资源关闭 释放 ResultSet, Statement, Connection。